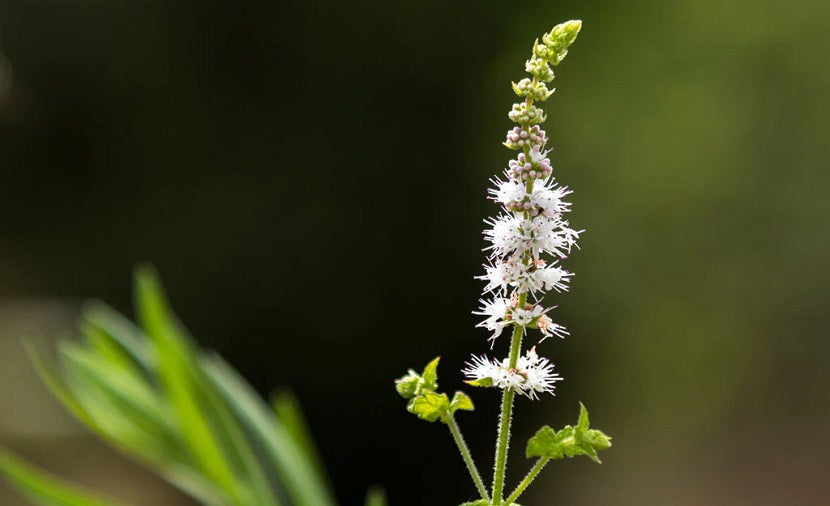
The benchmark in complementary medicines for regulating hormonal imbalances is an herbal medicine known as Cimicifuga Racemosa (Black Cohosh).
What is Black Cohosh (Cimicifuga)?
Cimicifuga is one of the most well-proven herbal medicines in the world today. It has been proven to be effective in a range of gynaecological complaints.
Pharmacological studies have demonstrated Cimicifuga Racemosa contains substances with endocrine activity, causing a selective reduction of the serum concentration of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) and is able to bind to oestrogen receptor sites.
It is assumed the active ingredient Triterpene Glycosides has an effect on the hypothalamus-pituitary system which leads to secondary effects on the reproductive and sympathetic/parasympathetic nervous systems. Numerous studies have proven Cimicifuga racemosa to be effective in hormonal complaints associated with premenstrual syndrome and menopause.
In one such study, Cimicifuga racemosa at a dose of 80mg per day was found to be effective in PMS, with freedom from symptoms in 84% of cases. This is a staggering percentage, considering the complex mechanisms of development for hormonal disorders.
Cimicifuga is also well known for its ability to effectively treat menopausal symptoms, with dozens of clinical trials to substantiate the action. In fact, Cimicifuga is the most popular complementary medicine for the treatment of menopause with millions of women worldwide benefiting from the hormonal regulatory affect.
Using the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), Cimicifuga Racemosa was shown to improve nervousness and irritability by 86.5 %; depressive moods by 82.5%; and sleeping problems by 76.8%. Stolze, H: Gyne 1, 14-16 (1982)
This regulating action can be demonstrated through the effectiveness of Cimicifuga in treating both menopausal symptoms and premenstrual symptoms.
Safety Concerns
A large meta-analysis has shown no incidence of liver reaction or disease due to taking black cohosh.
Conclusion: The results of this meta-analysis of five randomized, double-blind, and controlled clinical trials showed no evidence that iCR has any adverse effect on liver function.
Another two large-scale safety studies were concluded and found:
"Uncontrolled reports, postmarketing surveillance, and human clinical trials of more than 2,800 patients demonstrated a low incidence of adverse events (5.4%). Of the reported adverse events, 97% were minor and did not result in discontinuation of therapy, and the only severe events were not attributed to Cimicifuga treatment." PMID: 12851513

"Adverse symptoms have been rare (5,4%), mild and reversible. Most of them included gastrointestinal upsets, rashes, headaches, dizziness and mastalgia. Nevertheless, single cases of serious adverse events, including acute hepatocellular damage, have been reported, but without a clear causality relationship." PMID: 18592868
If you have not taken our online women's health assessment I strongly advise it to give you a better understanding what is occurring in your body and how to take proactive steps towards balancing your hormones naturally.








Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.