In short
-
The sympathetic nervous system drives our stress response ("fight or flight"), while the parasympathetic nervous system promotes calm and recovery ("rest and digest").
-
Prolonged sympathetic dominance-common in modern life-can lead to stress-related issues like poor digestion, sleep troubles, and fatigue.
-
Natural strategies such as deep breathing, mindfulness, gentle movement, and nutritional support can help rebalance the nervous system.
Our nervous system plays a crucial role in how we respond to stress. To comprehend this better, we first need to divide the nervous system into two main parts: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
-
Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
-
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch out from the CNS to the rest of the body.
The PNS is further divided into:
-
Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements and transmits sensory information.
-
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Regulates involuntary functions like heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.
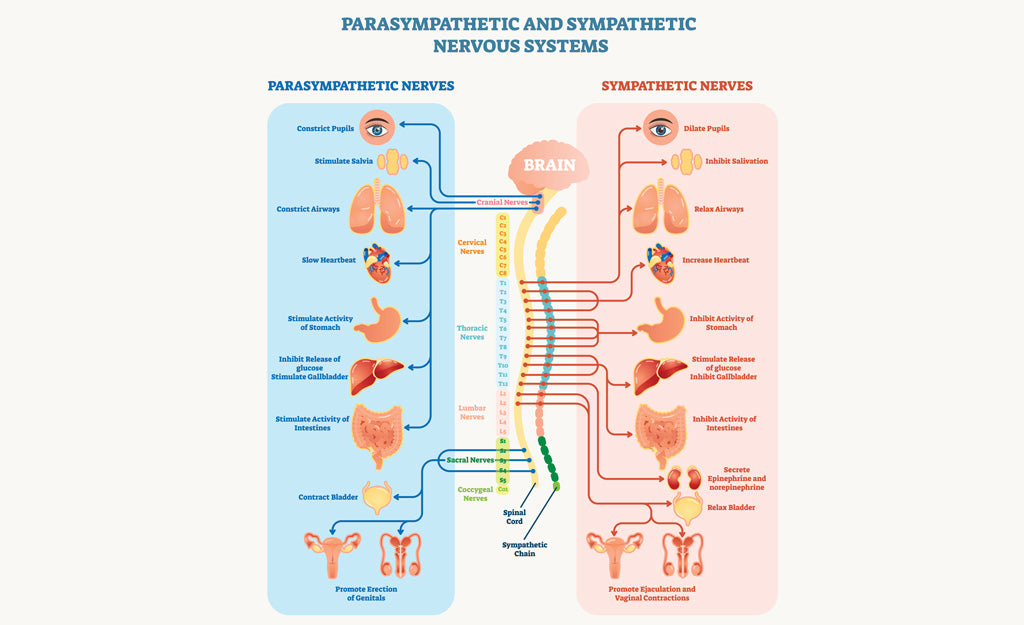
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Nervous System
The Autonomic Nervous System has two primary branches:
-
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Often referred to as the "fight or flight" system, it prepares the body to respond to perceived threats by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to muscles.
-
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): Known as the "rest and digest" system, it promotes relaxation, digestion, and recovery by slowing the heart rate and enhancing intestinal activity.
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System?
The sympathetic nervous system activates the body's rapid involuntary response to dangerous or stressful situations. A sudden release of hormones increases the heart rate, sharpens mental focus, and redirects energy to essential muscles.
What Does the Parasympathetic Nervous System Do?
The parasympathetic nervous system conserves energy by slowing down the heart rate, increasing intestinal and gland activity, and relaxing sphincter muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. It facilitates digestion, recovery, and overall relaxation.
Recognizing Sympathetic Dominance
In today's fast-paced world, many individuals experience prolonged sympathetic dominance, leading to various health issues:
-
Chronic Stress: Persistent activation of the SNS can result in anxiety, irritability, and mood swings.
-
Digestive Problems: Reduced blood flow to the digestive system can cause bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
-
Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep due to heightened alertness.
-
Fatigue: Constant energy expenditure without adequate recovery leads to exhaustion.
How to Activate the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Restoring balance between the SNS and PNS is essential for optimal health. Here are effective strategies to activate the parasympathetic nervous system:
1. Deep Breathing Exercises
Engaging in diaphragmatic or box breathing techniques can stimulate the vagus nerve, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
2. Meditation and Mindfulness
Regular meditation practices help calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and enhance parasympathetic activity.
3. Physical Activity
Gentle exercises like yoga, tai chi, or walking can shift the body from a sympathetic to a parasympathetic state.
4. Adequate Sleep
Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night allows the body to recover and maintain autonomic balance.
5. Nutrition and Hydration
Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods and staying hydrated supports overall nervous system health.
How to Calm the Sympathetic Nervous System
In addition to activating the PNS, it's important to directly calm the SNS:
-
Limit Stimulants: Reduce intake of caffeine and sugar, which can exacerbate SNS activity.
-
Establish a Routine: Consistent daily schedules can provide a sense of control and reduce stress.
-
Seek Social Support: Engaging with friends and loved ones can buffer stress responses.
Key takeaways
-
The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic (activates stress response) and parasympathetic (promotes relaxation) branches.
-
Chronic stress can disrupt this balance, leading to physical and emotional symptoms.
-
Activating the parasympathetic system through lifestyle practices can support calm, digestion, and recovery.
-
Supplements like Happy Calm and MSP | Magnesium, Sleep, Pain may aid in reducing stress and supporting nervous system health naturally.
Supporting Nervous System Health with Happy Healthy You
To further support your nervous system, consider incorporating the following products from Happy Healthy You:
Happy Calm: A natural supplement designed to alleviate stress and promote relaxation. It contains ingredients like Passionflower and Rhodiola, known for their calming properties.
MSP | Magnesium, Sleep, Pain: This comprehensive formula combines bioavailable magnesium with natural pain relievers and sleep-supporting herbs to enhance relaxation and recovery.